Prolotherapy
What is prolotherapy?
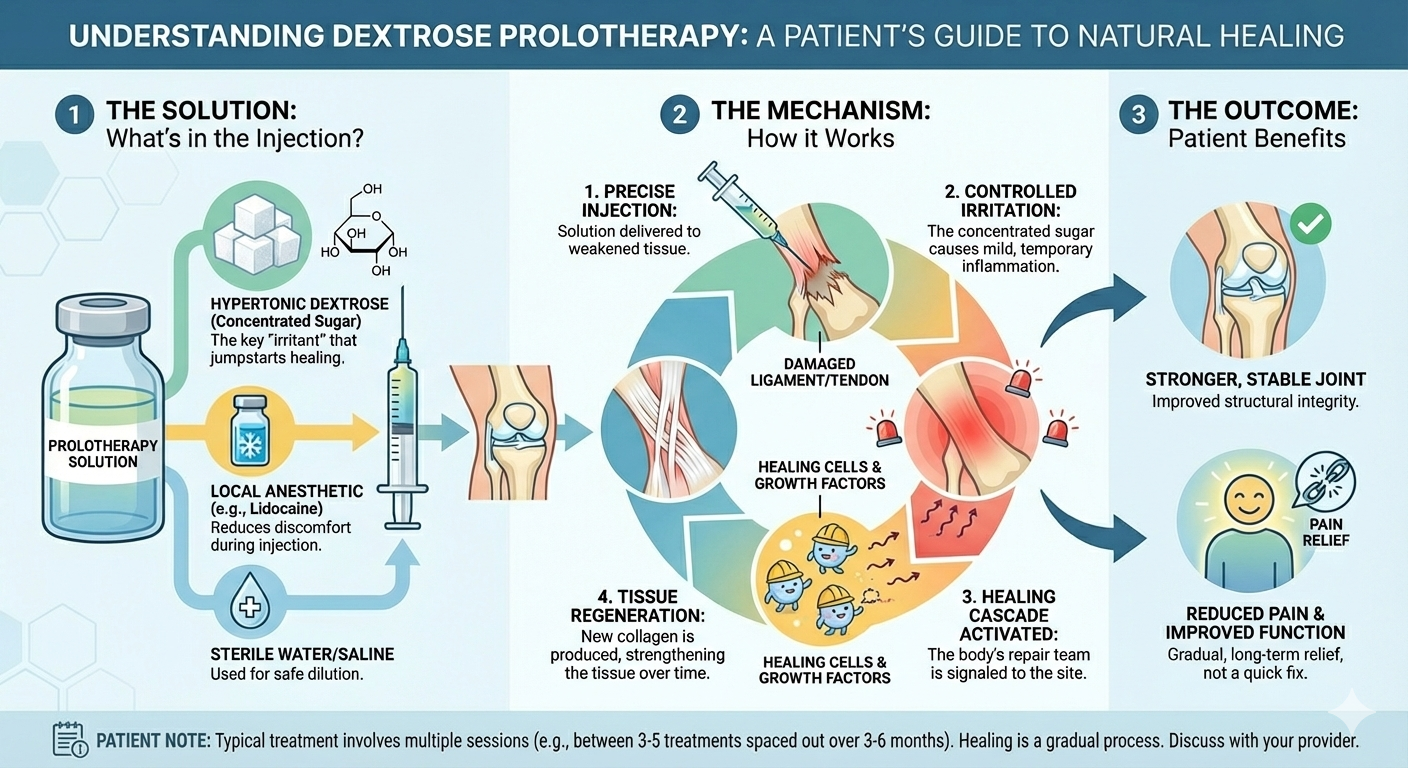
Prolotherapy is an injection-based treatment that involves injecting an irritant solution, most commonly hypertonic dextrose, into ligaments, tendons, or joints to stimulate tissue repair and reduce pain in chronic musculoskeletal conditions.[12]
What conditions is prolotherapy used for?
Prolotherapy has been studied for chronic soft tissue injuries, knee osteoarthritis, lateral epicondylosis (tennis elbow), plantar fasciopathy, Achilles tendinopathy, low back pain, and sacroiliac joint pain.[12][11]
How effective is prolotherapy?
For knee osteoarthritis, meta-analyses show prolotherapy provides greater pain reduction and functional improvement than placebo or exercise alone, with effects that may be dose- and time-dependent. [2][5][10-11]
For lateral elbow tendinosis, prolotherapy is superior to active controls in reducing pain and improving function at 12 weeks. [4]
For plantar fasciopathy, prolotherapy is superior to saline injections in the medium term, but corticosteroid injections are more effective for short-term pain relief. [9]
For chronic low back pain, prolotherapy may be effective in patients refractory to conservative therapy, though evidence is confounded by study heterogeneity and co-interventions. [6][8]
For other tendinopathies and ligament injuries, evidence is mixed, with some studies showing short-term benefit over corticosteroids, but insufficient high-quality data for definitive conclusions.[1][3][6]
How does prolotherapy compare to other treatments?
Prolotherapy generally shows comparable or modestly superior outcomes to non-injection therapies and placebo, and may be preferable to corticosteroid injections for some chronic conditions in the medium to long term, but is less effective than corticosteroids for short-term pain relief in plantar fasciopathy.[1][3-4][9]
What are the risks and side effects?
Prolotherapy is generally well tolerated, with no major adverse events reported in recent trials. Minor side effects may include transient pain or swelling at the injection site.[4-5][11]
What is the recommended protocol?
Protocols vary, but commonly involve injections at intervals of 2–4 weeks, with 3–6 sessions per course. Both intra-articular and extra-articular techniques are used, and combined approaches may enhance efficacy in knee osteoarthritis.[12][11]
Who are the best candidates for prolotherapy?
Patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain who have not responded to standard conservative treatments may be considered for prolotherapy, particularly for knee osteoarthritis, lateral epicondylosis, and chronic low back pain.[6-8][11]
Are there limitations to the evidence?
The quality of evidence is limited by heterogeneity, small sample sizes, and risk of bias in many studies. Further high-quality randomized controlled trials are needed to clarify optimal protocols and long-term efficacy.[1][3-5][9-10]
References
Hsu C, Vu K, Borg-Stein J.Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America. 2023;34(1):165-180. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2022.08.011.
Prolotherapy: A Clinical Review of Its Role in Treating Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain.
Distel LM, Best TM.PM & R : The Journal of Injury, Function, and Rehabilitation. 2011;3(6 Suppl 1):S78-81. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2011.04.003.
Prolotherapy for Osteoarthritis and Tendinopathy: A Descriptive Review.
Rabago D, Nourani B.Current Rheumatology Reports. 2017;19(6):34. doi:10.1007/s11926-017-0659-3.
Zhu M, Rabago D, Chung VC, et al.Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2022;103(11):2209-2218. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2022.01.166.
Chen YW, Lin YN, Chen HC, et al.Clinical Rehabilitation. 2022;36(6):740-752. doi:10.1177/02692155221086213.
Prolotherapy for Chronic Low Back Pain: A Review of Literature.
Giordano L, Murrell WD, Maffulli N.British Medical Bulletin. 2021;138(1):96-111. doi:10.1093/bmb/ldab004.
Fong HPY, Zhu MT, Rabago DP, et al.Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2023;104(11):1941-1953.e9. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2023.03.027.
Sit RWS, Wu RWK, Rabago D, et al.Annals of Family Medicine. 2020;18(3):235-242. doi:10.1370/afm.2520.
Sit RW, Chung VCh, Reeves KD, et al.Scientific Reports. 2016;6:25247. doi:10.1038/srep25247.
Efficacy of Prolotherapy for Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review.
Waluyo Y, Artika SR, Insani Nanda Wahyuni, Gunawan AMAK, Zainal ATF.Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 2023;55:jrm00372. doi:10.2340/jrm.v55.2572.
Goh SL, Jaafar Z, Gan YN, et al.PloS One. 2021;16(5):e0252204. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0252204.
Chung MW, Hsu CY, Chung WK, Lin YN.Medicine. 2020;99(46):e23201. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000023201.